Mainline Railways was a British model railway brand that operated between 1976 and 1983, introduced by Palitoy, the...
No products
Product successfully added to your shopping cart
There are 0 items in your cart. There is 1 item in your cart.
Search Tips
Open on Good Friday
The shop will be open on Friday 18th April.
Bring us some chocolate!
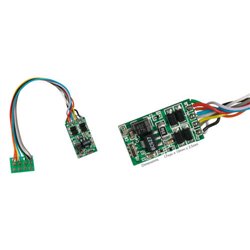
What are the common DCC decoders formats?
As the DCC standard is still evolving, there are several different sizes and formats for DCC decoders.
To give you an idea of the difference in pin numbers and their capabilities/functionality take a look at the list below of common DCC decoders:
6-pin (defined in NEM651 standard) with two functions.
8-pin (defined in NEM652 standard) with 2 or 3 functions.
18-pin (defined in NEM662) also called Next-18 with 6 function and ability to connect a stay-alive circuit.
21-pin (defined in NEM660) also called MTC-21 with 6 functions, ability to connect a stay-alive circuit and speaker.
Other types exist but are not widespread. For instance Hornby created a 4-pin decoder to fit in some of its smaller engines.
Click here to receive the tips weekly in your mailbox. You can unsubscribe at any time.